Pneumonia
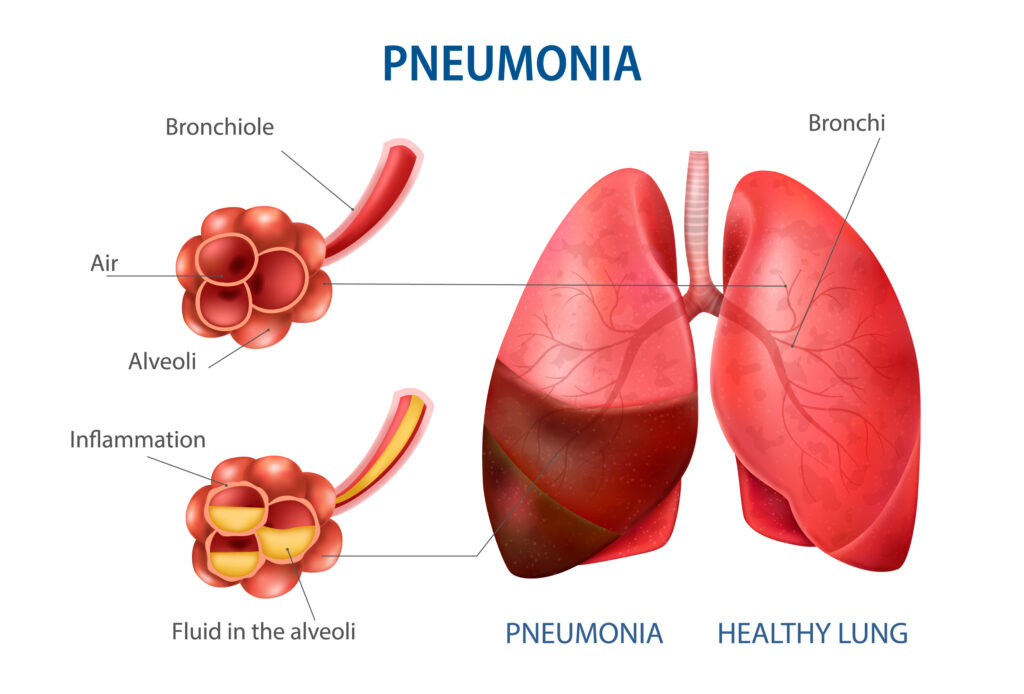
Pneumonia is a common lung infection characterized by inflammation of the air sacs in one or both lungs. Here are key points about pneumonia:
- Symptoms: Pneumonia symptoms include cough, fever, chills, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue, which can range from mild to severe depending on the individual and the type of pneumonia.
- Causes: Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms, with bacterial and viral pneumonia being the most common types.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves physical examination, chest X-ray, and sometimes blood tests or sputum cultures to identify the specific cause of pneumonia.
- Treatment: Treatment typically includes antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia, antiviral medications for viral pneumonia, rest, fluids, and sometimes supplemental oxygen or hospitalization for severe cases.
- Prevention: Preventive measures include vaccination against common pneumonia-causing pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and influenza virus, practicing good hygiene, quitting smoking, and avoiding exposure to respiratory irritants.
- Complications: Complications of pneumonia can include respiratory failure, sepsis, lung abscess, and pleural effusion, particularly in vulnerable populations such as young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential to reduce the risk of complications and facilitate recovery.
