Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
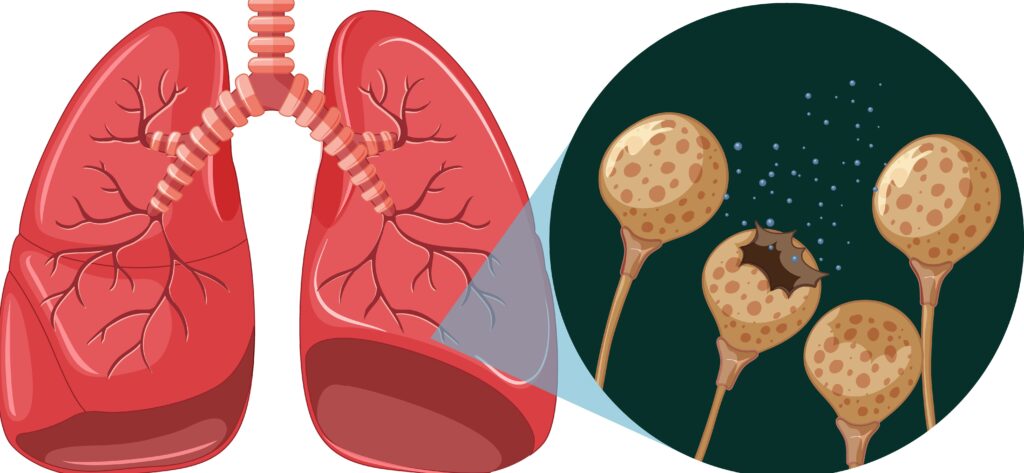
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition characterized by persistent airflow limitation. Here are key points about COPD:
- Symptoms: COPD symptoms include shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, and chest tightness.
- Causes: Smoking is the leading cause of COPD, though exposure to air pollutants, genetic factors, and respiratory infections also contribute.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves spirometry testing to assess lung function, along with medical history and imaging tests.
- Treatment: Management of COPD involves a combination of medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes.
- Prevention: Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to lung irritants can help prevent COPD or slow its progression.
- Complications: COPD can lead to complications such as respiratory infections, heart problems, and worsening respiratory function over time.
- Prognosis: While COPD is a progressive disease with no cure, early detection and appropriate management can improve quality of life and slow disease progression.
