Bronchiectasis
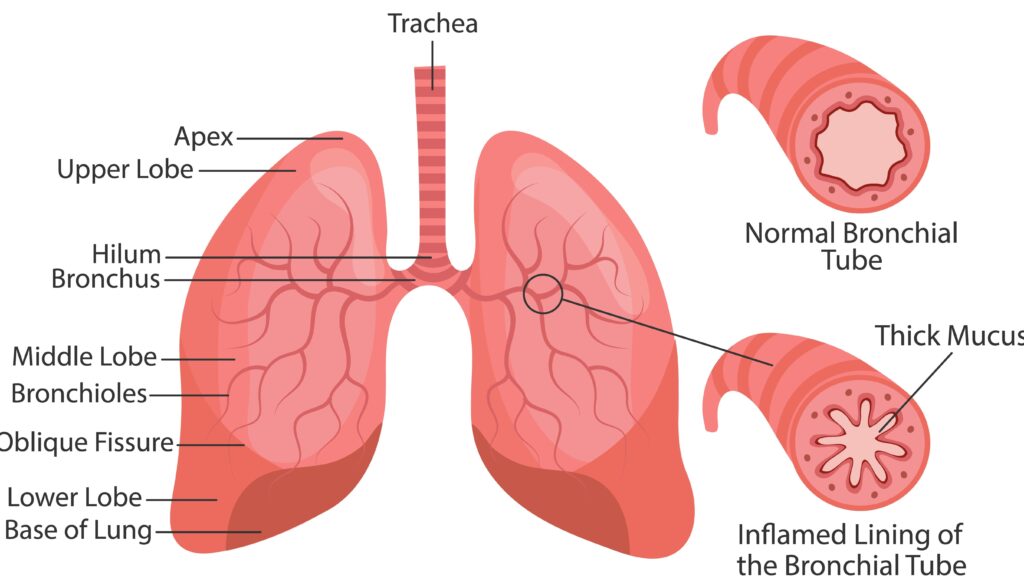
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition characterized by irreversible widening and scarring of the airways, leading to recurrent respiratory infections and difficulty clearing mucus. Here are key points about bronchiectasis:
- Symptoms: Symptoms of bronchiectasis include chronic cough, excess mucus production, recurrent chest infections, shortness of breath, fatigue, and wheezing.
- Causes: Bronchiectasis can result from various underlying conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, respiratory infections, immune system disorders, or inhalation of toxic substances.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves imaging tests like CT scans, lung function tests, sputum cultures, and bronchoscopy to assess the extent of airway damage and identify potential causes.
- Treatment: Treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and manage underlying causes. This may include airway clearance techniques, bronchodilators, antibiotics for infections, inhaled corticosteroids, and, in severe cases, surgical removal of damaged lung tissue.
- Management: Effective management of bronchiectasis involves a multidisciplinary approach, including pulmonary rehabilitation, nutritional support, vaccinations against respiratory infections, and regular monitoring to prevent exacerbations and improve quality of life.
- Complications: Complications of bronchiectasis can include respiratory failure, recurrent infections, lung abscesses, and progressive lung damage, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and comprehensive management strategies to minimize long-term complications.
