Tuberculosis (TB)
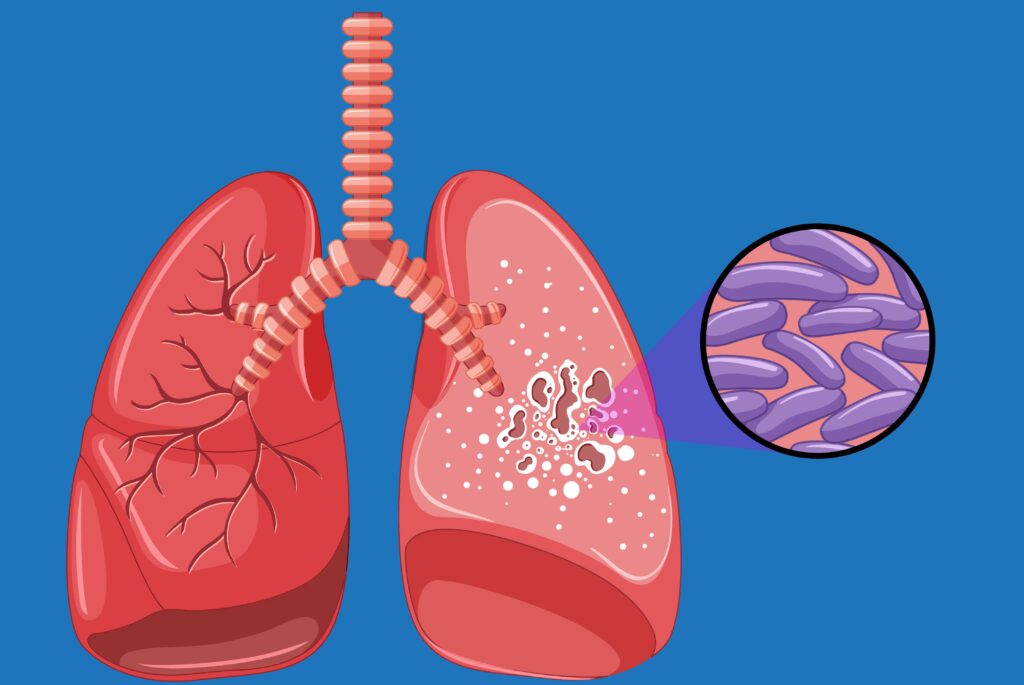
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection primarily affecting the lungs but can also target other parts of the body. Here are key points about TB:
- Symptoms: Common symptoms of TB include persistent cough, chest pain, weight loss, fatigue, fever, and night sweats.
- Transmission: TB spreads through the air when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or speaks, making it highly contagious.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves TB skin tests, blood tests, chest X-rays, and sputum tests to detect the presence of the bacteria.
- Treatment: Treatment for TB typically involves a combination of antibiotics taken over several months to eradicate the bacteria and prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
- Prevention: Preventive measures include vaccination with the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, identification and treatment of latent TB infections, and infection control measures to limit the spread of TB in communities.
- Global Impact: TB remains a significant global health concern, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, where factors such as poverty, malnutrition, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure contribute to its prevalence.
- Challenges: Challenges in TB control include drug resistance, limited access to healthcare services, stigma associated with the disease, and the need for improved diagnostics and treatment options to effectively combat the spread of TB worldwide.
