Asthma
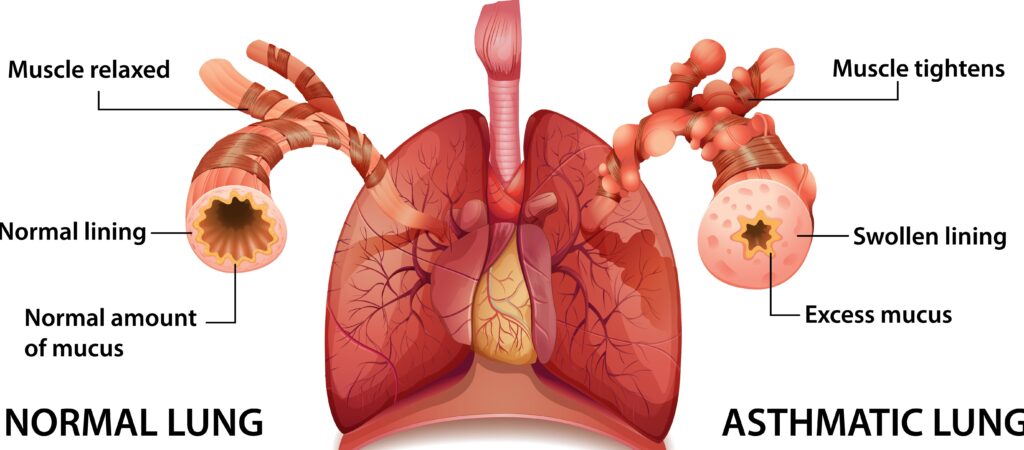
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Here are key points about asthma:
- Symptoms: Asthma symptoms include wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing, which may vary in severity and frequency.
- Triggers: Asthma symptoms can be triggered by various factors, including allergens (such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander), respiratory infections, exercise, cold air, and irritants (like smoke or strong odors).
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves assessing symptoms, lung function tests (such as spirometry), and sometimes allergy testing to identify triggers.
- Treatment: Management of asthma typically includes long-term control medications (such as inhaled corticosteroids or bronchodilators) to reduce inflammation and prevent symptoms, as well as quick-relief medications (like rescue inhalers) to provide immediate relief during flare-ups.
- Prevention: Asthma management also involves avoiding triggers whenever possible and following an asthma action plan provided by healthcare providers to effectively manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations.
- Complications: Poorly controlled asthma can lead to frequent flare-ups, decreased lung function, and increased risk of respiratory infections, so it’s essential to manage the condition effectively to prevent complications and maintain optimal lung health.
